|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
AI agents are software systems designed to perceive their environment, reason about it, and take actions autonomously to achieve defined goals. Unlike traditional programs that execute fixed instructions, AI agents operate continuously, adapt to changing inputs, and make decisions without constant human intervention.
In simple terms:
- Traditional software → waits for input, returns output
- AI agent → observes, thinks, decides, acts, and learns
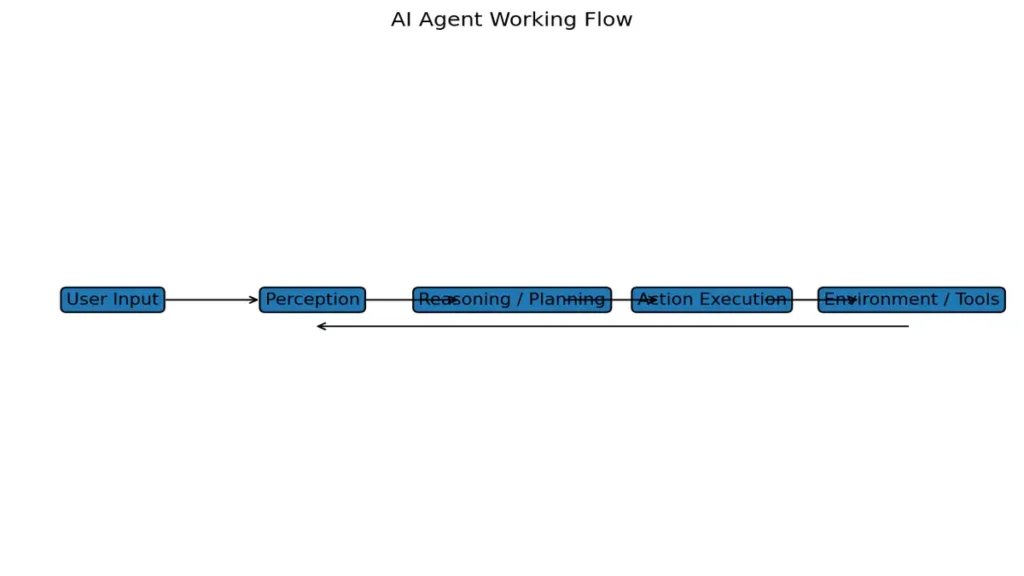
Core Components of an AI Agent
An AI agent is typically built using the following layers:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Perception | Collects data from the environment (APIs, sensors, user input, logs) |
| State / Memory | Stores context, history, and intermediate reasoning |
| Reasoning Engine | Decides what action to take (rules, ML models, LLMs) |
| Action Module | Executes tasks (API calls, database updates, UI actions) |
| Feedback Loop | Evaluates outcomes and improves future decisions |
How AI Agents Work (Step-by-Step)
- Sense – The agent receives signals (user queries, system events, web data).
- Interpret – Converts raw input into structured understanding.
- Plan – Breaks a goal into smaller executable steps.
- Act – Executes actions using tools, APIs, or code.
- Learn – Adjusts behavior based on success or failure.
This loop runs continuously, making agents suitable for long-running tasks.
Types of AI Agents
1. Reactive Agents
Respond instantly to inputs without memory.
- Example: Spam filters
- Limitation: No learning or planning
2. Goal-Based Agents
Act to achieve specific objectives.
- Example: Route optimization systems
- Strength: Strategic decision-making
3. Utility-Based Agents
Choose actions that maximize a utility score.
- Example: Recommendation engines
- Strength: Optimization under constraints
4. Learning Agents
Improve over time using feedback.
- Example: Autonomous trading bots
- Strength: Adaptability
5. LLM-Powered Agents
Use large language models for reasoning and planning.
- Example: AI coding assistants, research agents
- Strength: General intelligence across domains
AI Agents vs Traditional AI Models
| Feature | Traditional AI | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Low | High |
| Memory | Limited | Persistent |
| Tool Usage | None | Extensive |
| Continuous Operation | No | Yes |
| Goal Execution | Single-step | Multi-step |
AI Agents vs Chatbots
Chatbots answer questions.
AI agents get work done.
| Aspect | Chatbot | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Task Scope | Single response | End-to-end workflow |
| Context | Short-term | Long-term |
| Tool Integration | Minimal | Advanced |
| Decision Making | Limited | Autonomous |
Real-World Use Cases
Software Development
- Code generation and refactoring
- CI/CD automation
- Bug detection
Marketing & SEO
- Keyword research
- Content planning
- A/B testing automation
Customer Support
- Ticket triaging
- Automated resolutions
- CRM updates
Finance
- Fraud detection
- Algorithmic trading
- Risk analysis
DevOps
- Infrastructure monitoring
- Auto-scaling decisions
- Incident response
Popular AI Agent Frameworks
| Framework | Purpose |
|---|---|
| LangChain | Tool-based LLM agents |
| Auto-GPT | Autonomous task execution |
| CrewAI | Multi-agent collaboration |
| OpenAI Assistants API | Tool-enabled AI agents |
| Semantic Kernel | Agent orchestration |
Single-Agent vs Multi-Agent Systems
Single-Agent
- One agent handles all tasks
- Easier to manage
- Limited scalability
Multi-Agent
- Multiple specialized agents collaborate
- Higher efficiency
- Used in complex workflows (research, trading, simulations)
Architecture Example (High-Level)
User Request → Planner Agent → Tool Agent → Execution → Memory Update → Feedback
This modular approach improves scalability and reliability.
Risks and Limitations
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Hallucinations | Incorrect reasoning or outputs |
| Security | Tool misuse or data leakage |
| Cost | High compute and API usage |
| Control | Hard to predict autonomous behavior |
Mitigation requires monitoring, guardrails, and human oversight.
Future of AI Agents
AI agents are moving toward:
- Self-improving architectures
- Real-time decision systems
- Enterprise-wide automation
- Agent-to-agent communication standards
They are expected to become the core execution layer of modern software systems.
Key Takeaways
- AI agents are autonomous, goal-driven systems
- They go beyond chatbots and static AI models
- They enable end-to-end automation
- Adoption is accelerating across industries
Further Reading
Arsalan Malik is a passionate Software Engineer and the Founder of Makemychance.com. A proud CDAC-qualified developer, Arsalan specializes in full-stack web development, with expertise in technologies like Node.js, PHP, WordPress, React, and modern CSS frameworks.
He actively shares his knowledge and insights with the developer community on platforms like Dev.to and engages with professionals worldwide through LinkedIn.
Arsalan believes in building real-world projects that not only solve problems but also educate and empower users. His mission is to make technology simple, accessible, and impactful for everyone.
Join us on dev community