|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
Introduction
Monolith and Microservices are two dominant software architecture patterns used to build modern applications. Choosing the right one impacts scalability, performance, development speed, and long-term maintenance. This article explains both approaches in a clear, practical way, with real-world trade-offs.
What Is Monolithic Architecture?
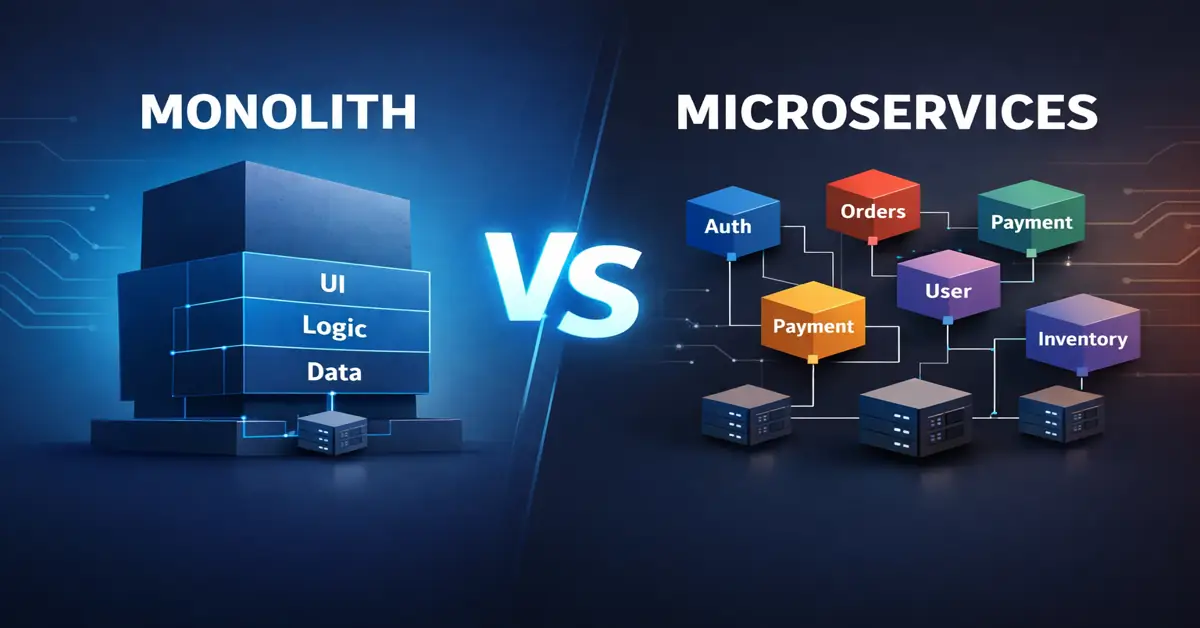
A Monolithic Architecture is a single, unified application where all components—UI, business logic, and database access—are tightly coupled and deployed together.
Example: A traditional PHP or Java web application where authentication, payments, and user management run as one codebase.
To understand the basics of monolithic systems, you can refer to this explanation on Martin Fowler.
Key Characteristics
- Single codebase
- Single deployment unit
- Shared database
- Tight coupling between modules
What Is Microservices Architecture?
Microservices Architecture breaks an application into small, independent services. Each service handles a specific business function and communicates via APIs.
Example: Separate services for authentication, payments, notifications, and analytics.
A good conceptual overview is available on AWS Microservices Guide.
Key Characteristics
- Independent services
- Separate deployments
- Decentralized data management
- API-based communication (REST, gRPC, events)
Monolith vs Microservices: Comparison Table
| Feature | Monolithic Architecture | Microservices Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Codebase | Single | Multiple services |
| Deployment | One unit | Independent deployments |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
| Performance | Faster for small apps | Network overhead |
| Development Speed | Faster initially | Slower setup |
| Maintenance | Difficult as app grows | Easier long-term |
| Technology Stack | Usually one stack | Multiple stacks |
| Fault Isolation | Poor | Strong |
Advantages of Monolithic Architecture
- Simple to develop and deploy
- Easier debugging and testing
- Better performance for small-scale apps
- Ideal for MVPs and startups
More details on monolith pros are explained well on GeeksforGeeks.
Disadvantages of Monolithic Architecture
- Hard to scale individual features
- Risky deployments
- Difficult to maintain large codebases
- Technology lock-in
Advantages of Microservices Architecture
- Independent scaling of services
- Faster innovation
- Better fault tolerance
- Teams can work independently
A practical breakdown can be found on Microservices.io.
Disadvantages of Microservices Architecture
- Complex system design
- Requires DevOps, CI/CD, monitoring
- Network latency issues
- Higher infrastructure cost
When Should You Use Monolith?
Choose monolithic architecture if:
- You are building an MVP
- The team is small
- The application logic is simple
- Time-to-market is critical
When Should You Use Microservices?
Choose microservices if:
- The application is large and complex
- You need high scalability
- Multiple teams work in parallel
- You expect frequent feature updates
Real-World Usage Examples
- Monolith: WordPress, early-stage SaaS apps
- Microservices: Netflix, Amazon, Uber
Netflix’s transition is discussed in detail on Netflix Tech Blog.
FAQs
Is microservices always better than monolith?
No. Microservices add complexity and are not ideal for small or simple applications.
Can a monolith be converted into microservices later?
Yes. Many companies start with monolith and gradually break it into services using the strangler pattern.
Which architecture is better for startups?
Monolith is usually better for startups due to speed and simplicity.
Do microservices require containers?
Not mandatory, but tools like Docker and Kubernetes make microservices easier to manage.
Conclusion
Monolith and Microservices both have valid use cases. Monolith works best for simplicity and speed, while Microservices excel at scale and long-term growth. The right choice depends on team size, application complexity, and future plans.
Arsalan Malik is a passionate Software Engineer and the Founder of Makemychance.com. A proud CDAC-qualified developer, Arsalan specializes in full-stack web development, with expertise in technologies like Node.js, PHP, WordPress, React, and modern CSS frameworks.
He actively shares his knowledge and insights with the developer community on platforms like Dev.to and engages with professionals worldwide through LinkedIn.
Arsalan believes in building real-world projects that not only solve problems but also educate and empower users. His mission is to make technology simple, accessible, and impactful for everyone.
Join us on dev community